The Space Shuttle Missions
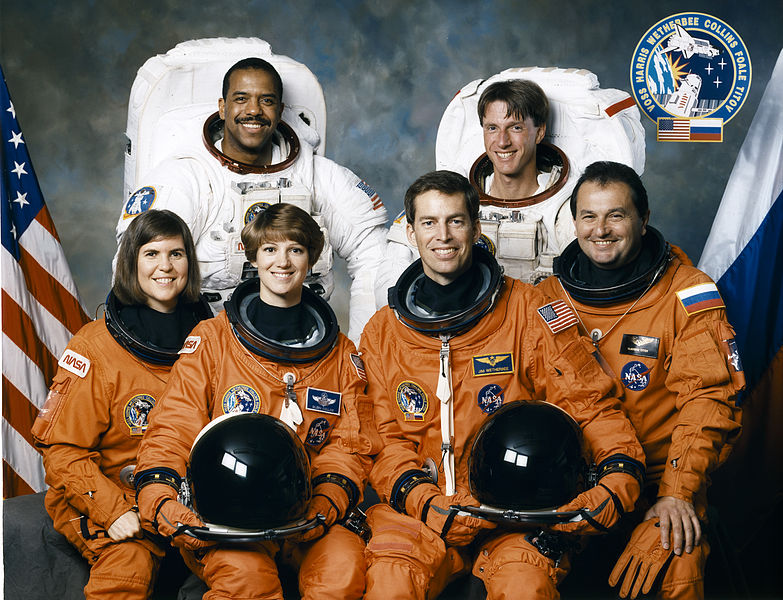
James D. Wetherbee
(Third Space Flight)
Eileen Collins
(Second Space Flight) Mission Specialist 1:
Michael Foale
(Third Space Flight) Mission Specialist 2:
Bernard A. Harris Jr.
(Second Space Flight) Mission Specialist 3:
Janice E. Voss
(Third Space Flight) Mission Specialist 4:
Vladmir G. Titov, RKA
(FirstSpace Flight)
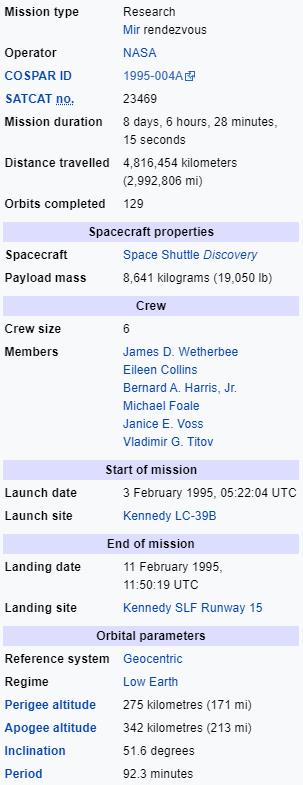
STS-63 was the second mission of the US/Russian Shittle-Mir Programme, which carried out the first rendezvous of the American Space Shuttlewith Russia's space station Mir. Known as the 'Near-Mir' mission, the flight used Space Shuttle Discovery which lifted off from launch pad 39B on 3 February 1995 from Kennedy Space Centre, Florida. A night launch and the 20th mission for Discovery, it marked the first time a Space Shuttle mission had a female pilot, Eileen Collins, and carried out the successful deployment and retrieval of the Spartan-204 platform, along with the scheduled rendezvous and flyaround of Mir, in preparation for STS-71, the first mission to dock with Mir.
A free template by Lucknowwebs.com for WYSIWYG WebBuilder 8
Study
Research
Main Index
Space Cosmology
Science Research
*
About
Science Research
Science Theories
Desk
Site Map
BookShelf
Copyright © by Nigel G Wilcox · All Rights reserved · E-Mail: ngwilcox100@gmail.com
Designed by Nigel G Wilcox
Powered By AM3L1A
Pages within this section: USA Shuttle Mission Flights
STS-63
Pages within this section:
The Space Shuttle Missions
Astronauts:
STS-63
Command Pilot:
Pilot:
61m
M
8
SM
Sub-Menu
menu
-
62
62a
63
64
65
66
67


Payloads flying aboard STS-63 included the Cryo Systems Experiment (CSE), the Shuttle Glow (GLO-2) experiment, Orbital Debris Radar Calibration Spheres (ODERACS-2), the Solid Surface Combustion Experiment (SSCE), the Air Force Maui Optical Site Calibration Test (AMOS) and the Midcourse Space Experiment (MSX).
Beginning on flight day one, a series of thruster burns were performed daily to bring Discovery in line with Mir. The original plan called for the orbiter to approach to no closer than 10 meters (33 ft) from Mir, and then complete a flyaround of the Russian space station. However, three of the 44 orbiter Reaction Control System (RCS) thrusters—small firing jets used for on-orbit maneuvering—sprang leaks prior to rendezvous. Shortly after main engine cutoff, two leaks occurred in the aft primary thrusters, one of which—called R1U—was key to rendezvous. A third leak occurred later in flight in the forward primary thruster, but the crew was able to fix the problem.
After extensive negotiations and technical information exchanges between the U.S. and Russian space teams, the Russians concluded close approach could be safely achieved and the STS-63 crew was given 'go' to proceed. R1U's thruster manifold was closed and the backup thruster was selected for the approach. Ship-to-ship radio contact with Mir was achieved well ahead of time, and Titov, who had previously lived on Mir for more than a year, communicated excitedly with the three cosmonauts aboard the space station: Mir 17 Commander Alexander Viktorenko; Flight Engineer Yelena Kondakova; and Valery Polyakov, a physician who had broken Titov's record for extended time in space
The crew also worked extensively with payloads aboard Discovery. Flying in the forward payload bay and activated on flight day one was SPACEHAB-3. The commercially developed module was making its third flight on the Shuttle and carried 20 experiments: 11 biotechnology experiments, three advanced materials development experiments, four technology demonstrations and two pieces of supporting hardware measuring on-orbit accelerations. Improvements had been made to the SPACEHAB system to reduce demand on crew time. A new video switch had been added to lessen the need for astronaut involvement in video operations, and an experiment interface had been added to the telemetry system to allow the experiment investigator to link directly via computer with the onboard experiment to receive data and monitor status.
Among the plant growth experiments was Astroculture, flying for the fourth time on the Shuttle. The objective of Astroculture was to validate performance of plant growth technologies in the microgravity environment of space for application to a life support system in space. The investigation had applications on Earth, since it covered such topics as energy-efficient lighting and removal of pollutants from indoor air. One of the pharmaceutical experiments, Immune, also had Earth applications. Exploiting a known tendency of spaceflight to weaken the immune system, the Immune experiment tested the ability of a particular substance to prevent or reduce this weakening. Clinical applications could include treatment of individuals suffering from such immunosuppressant diseases as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
STS-63's primary objective was to perform a rendezvous and fly around the Russian space station Mir. The objectives of the Mir rendezvous were to verify flight techniques, communications and navigation aid sensor interfaces, and engineering analyses associated with Shuttle/Mir proximity operations in preparation for the STS-71 docking mission.
Other objectives of the flight were to perform the operations necessary to fulfill the requirements of experiments located in SPACEHAB-3 and to fly captively, then deploy and retrieve the Spartan-204 payload. Spartan-204, the Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research Tool for Astronomy, was a free-flying retrievable platform. It was designed to obtain data in the far ultraviolet region of the spectrum from diffuse sources of light. Two crewmembers were scheduled to perform a five-hour spacewalk.















