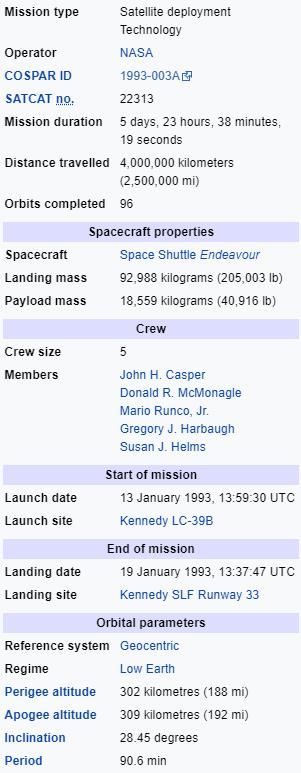
John H. Casper
(Second Space Flight)
Donald R. McMonagle
(Second Space Flight) Mission Specialist 1:
Mario Runco Jr.
(Second Space Flight) Mission Specialist 2:
Gregory J. Harbaugh
(First Space Flight) Mission Specialist 3:
Susan J. Helms
(Second Space Flight)
STS-54 Shuttle mission was a Space Transportation System (NASA Space Shuttle) mission using orbiter Endeavour. This was the third flight for Endeavour, and launched 13 January 1993. The primary payload was the fifth Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-F) which was deployed on day one of the mission. It was later successfully transferred to its proper orbit by the Inertial Upper Stage booster.
Also carried into orbit in the payload bay was a Hitchhiker experiment called the Diffuse X-ray Spectrometer (DXS). This instrument collected data on X-ray radiation from diffuse sources in deep space.
A free template by Lucknowwebs.com for WYSIWYG WebBuilder 8
Study
Research
Main Index
Space Cosmology
Science Research
*
About
Science Research
Science Theories
Desk
Site Map
BookShelf
Copyright © by Nigel G Wilcox · All Rights reserved · E-Mail: ngwilcox100@gmail.com
Designed by Nigel G Wilcox
Powered By AM3L1A
Pages within this section: USA Shuttle Mission Flights
STS-54
Pages within this section:
The Space Shuttle Missions
Astronauts:
STS-54
Command Pilot:
Pilot:
53
M
8
SM
Sub-Menu
menu
-
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
Other middeck payloads to test the effects of microgravity included the Commercial General Bioprocessing Apparatus (CGPA) for-life sciences research; the Chromosome and Plant Cell Division in Space Experiment (CHROMEX) to-study plant growth; the Physiological and Anatomical Rodent Experiment (PARE) to examine the skeletal system and the adaptation of bone to space flight; the Space Acceleration Measurement Equipment (SAMS) to measure and record the microgravity acceleration environment of middeck experiments; and the Solid Surface Combustion Experiment (SSCE) to measure the rate of flame spread and temperature of burning filter paper.
Also, on day five, mission specialists Mario Runco and Gregory J. Harbaugh spent nearly 5 hours in the open cargo bay performing a series of space-walking tasks designed to increase NASA's knowledge of working in space. They tested their abilities to move about freely in the cargo bay, climb into foot restraints without using their hands and simulated carrying large objects in the microgravity environment.

Harbaugh and Runco during the EVA
Endeavour deploys the TDRS-F satellite
















