A free template by Lucknowwebs.com for WYSIWYG WebBuilder 8
Powered by Sispro1-S
Nigel G Wilcox
Paragon Of Space Publication
© Copyright Reserved - United Kingdom
Ideal Screen Composition 1024 x 768
SITEMAP
SCIENCE RESEARCH
ABOUT
Desk
Supersonic
Stealth
MAIN INDEX
Sea-Air Planes
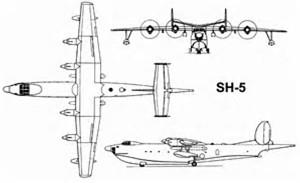
SH-5 Harbin Seaplane
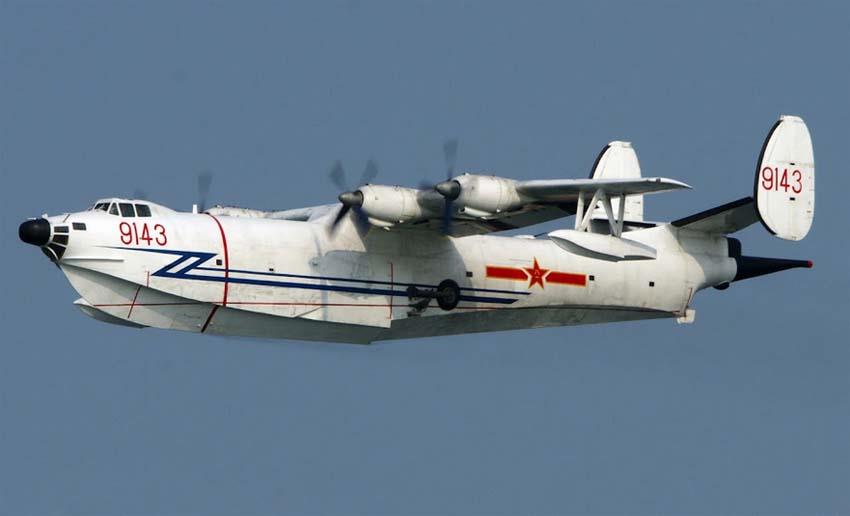
The Harbin SH-5 is a Chinese maritime patrol amphibious aircraft intended for a wide range of duties, including aerial firefighting, anti-submarine warfare and air-sea rescue. One prototype and six production aircraft have been built.
Maximum speed: 556 km/h (345.48 mph) Length: 127.62 ft Wingspan: 118.11 ft Manufacturer: Harbin Aircraft Industry Group
General characteristics
Crew: 8
Capacity: 10,000 kg (22,000 lb) maximum payload (cargo), 6,000 kg (13,000 lb) maximum weapons load
Length: 38.9 m (127 ft 7 in)
Wingspan: 36 m (118 ft 1 in)
Height: 9.79 m (32 ft 1 in)
Wing area: 144 m2 (1,550 sq ft)
Empty weight: 25,000 kg (55,116 lb) SAR (Search And Rescue) and Transport
26,500 kg (58,400 lb) ASW (Anti-Submarine Warfare)
Gross weight: 36,000 kg (79,366 lb)
Max takeoff weight: 45,000 kg (99,208 lb)
Fuel capacity: 16,500 kg (36,400 lb) max
Powerplant: 4 × Dongan WJ5A turboprop engines, 2,350 kW (3,150 hp) each
Propellers: 4-bladed constant speed reversible propellers, 3.8 m (12 ft 6 in) diameter
Performance
Maximum speed: 556 km/h; 345 mph (300 kn)
Cruise speed: 450 km/h; 280 mph (243 kn) maximum
Min Patrol speed: 230 km/h (120 kn; 140 mph)
Take-off speed (water): 160 km/h (86 kn; 99 mph)
Landing speed (water): 92 km/h (50 kn; 57 mph)
Range: 4,756 km; 2,955 mi (2,568 nmi) with maximum fuel
Endurance: 15 hours on two engines
Service ceiling: 10,250 m (33,630 ft) service ceiling
Rate of climb: 9 m/s (1,800 ft/min)
Wing loading: 250 kg/m2 (51 lb/sq ft) at 36,000 kg (79,000 lb)
312.5 kg/m² (64 lb/sqft) at 45,000 kg (99,000 lb)
Power/mass: 0.302 kW/kg (0.184 hp/lb) at 36,000 kg (79,000 lb)
0.242 kW/kg (0.147 hp/lb) at 45,000 kg (99,000 lb)
Take-off run (water): 548 m (1,798 ft)
Landing run (water): 240 m (790 ft)
Armament
four hardpoints; 6,000 kg (13,000 lb) warload; C-101 ASMs, ASW torpedoes, depth charges; mines; bombs
Avionics
Doppler search radar in nose radome; MAD (Magnetic Anomaly Detector) boom extending from the tail of the fuselage




While the Japanese were developing the PS-1, the Chinese began work on a comparable aircraft. In early 1970, after several years of consideration of various preliminary designs, the Harbin Aircraft Manufacturing Corporation (HAMC) and the Chinese Seaplane Design Institute began formal work on a four-turboprop flying boat that could be used for maritime warfare, SAR, and cargo transport roles. The aircraft was to be designated the "Maritime Bomber 5 (Shuishang Hongzhaji 5 / SH-5)", though sources mention an alternate "PS-5" designation.
A static test airframe was completed in 1971, but due to the upheaval of the Chinese "Cultural Revolution", did not begin tests until August 1974. In the meantime, a flying prototype had been rolled out in December 1973, beginning taxi trials in May 1975 and performing its first flight on 3 April 1976.
The slow pace of the program continued, a single production batch of six aircraft being completed in 1984 and 1985, with four of them handed over to the People's Liberation Army Naval Air Force in 1986. They have been retained in service, and may have received some combat electronic system updates.
The SH-5 has a very general resemblance to the PS-1 / US-1, with a long, relatively slender, fuselage and hull, a high wing with four turboprops, and a fixed float near each wingtip. However, in detail it shows clear influence of Soviet Beriev flying boat designs, with a twin-fin tail and very similar nose layout.
The SH-5 is powered by four Dongan WJ5A turboprop engines with 3,150 horsepower each, driving four-bladed propellers. The aircraft is a pure seaplane, though it does have built-in beaching gear roughly similar to that of the PS-1. There are spray-suppression strakes on each side of the nose, and a small sea rudder at the rear of the hull.
The SH-5 is armed with a dorsal turret mounting twin cannon, and there are two stores pylons on each wing, one placed between the hull and the inboard engine, the second placed between the inboard and outboard engines. These four stores pylons can each be fitted with a C-101 antishipping missile, or each of the outer stores pylons can be fitted with three homing torpedoes.
Six tonnes (13,200 pounds) of other stores, such as depth charges, mines, bombs, sonobuoys, or rescue gear can be stored in a rear compartment in the fuselage. A Doppler search radar is fitted in a thimble radome in the nose, and a fixed MAD boom is fitted to the tail. If configured as a cargolifter, the SH-5 can carry 10 tonnes (22,000 pounds) of cargo.
The SH-5 carries a flight crew of eight, including a pilot; co-pilot; navigator; flight engineer; radio operator; and three systems specialists. The number of specialists may vary depending on the mission.
The fuselage is unpressurized. There are three freight compartments behind the cockpit area, followed by a cabin for the mission crew, a compartment for communications gear, and finally the stores compartment. There is a corridor connecting all three compartments, with watertight doors into the compartments. There is one crew door on the left side of the aircraft and two on the right.
Role: Maritime patrol amphibian/air-sea rescue
Manufacturer: Harbin Aircraft Factory
First flight: 3 April 1976
Introduction: 1986
Primary user: People's Liberation Army Naval Air Force
Produced: 1984-1985
Number built: 7
S'sonic
Stealth
Menu
Space
Transport
Menu
Topic
Menu
Study
Menu