S'sonic
Stealth
Menu
A free template by Lucknowwebs.com for WYSIWYG WebBuilder 8
Powered by Sispro1-S
Nigel G Wilcox
Paragon Of Space Publication
© Copyright Reserved - United Kingdom
Ideal Screen Composition 1024 x 768
SITEMAP
PSEUDO SCIENCE
SCIENCE RESEARCH
ABOUT
Desk
Supersonic
Stealth
Study
Menu
MAIN INDEX
Fastest Air Planes
Space
Transport
Menu
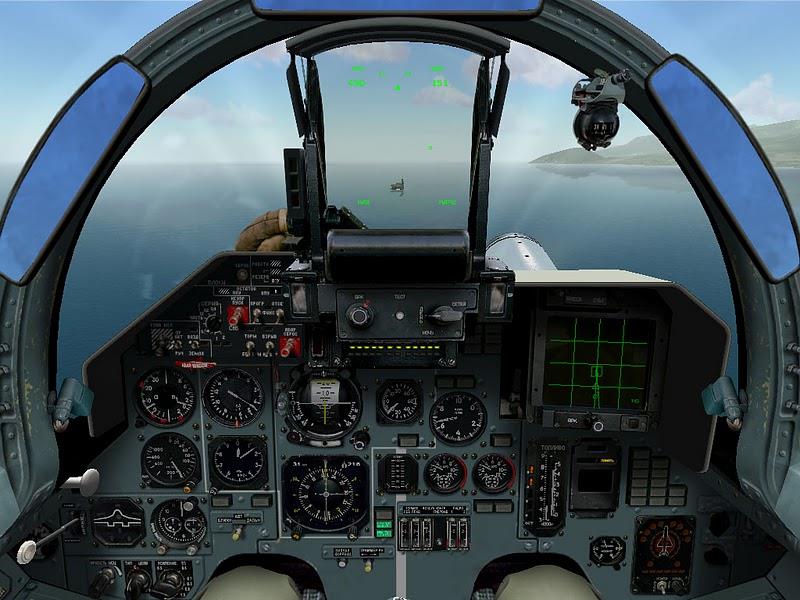
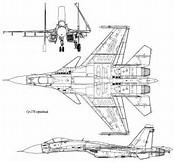
Sukhoi SU-33 (Flying Shark)
The Chinese navy also conducted carrier-based operations with its new Shenyang J-15 Flying Shark unlicensed derivative of the Sukhoi Su-33 Flanker in 2013. By September of last year, the report notes that PLAN pilots flying the J-15 were conducting full-stops and takeoffs with weapon loads at full maximum gross weights onboard the carrier Liaoning. “Although the J-15 has a land-based combat radius of 1,200 km, the aircraft will be limited in range and armament when operating from the carrier, because the ski-jump design does not provide as much airspeed and, therefore, lift at takeoff as a catapult design,” the report notes.
Maximum speed: 2,300 km/h (1,429 mph), Range: 1,864 mi, Maiden flight: 17 Aug 1987, Length: 71.98 ft, Wingspan: 48.25 ft, Cruising speed: 1,400 km/h (869.92 mph).
The Sukhoi Su-33 is an all-weather carrier-based twin-engine air superiority fighter designed by Sukhoi and manufactured by Komsomolsk-on-Amur Aircraft Production Association, derived from the Su-27 and initially known as the Su-27K. Compared with the Su-27, the Su-33 has a strengthened undercarriage and structure, folding wings and stabilators, all for carrier operations. The Su-33 has canards and its wings are larger than the Su-27 for increased lift. The Su-33 has upgraded engines and a twin nose wheel, and is air refuelable.
The Sukhoi Su-33 was designed primarily for use on the Russian Admiral Kuznetsov heavy aviation cruiser. It evolved from the Su-27. Originally the shipborne version was known as Su-27K, but later redesignated to Su-33. The Su-33 is an air-superiority fighter. Western reporting name of the aircraft is Flanker-D. Its production began in 1985 in the Soviet Union. The Su-33 made its maiden flight in 1987, but the official introduction to the Russian Navy was only in 1998. It seems that production was stopped in 1997.
Production of this aircraft goes slowly. The reason is a high cost and the fact that this Su-33 is carrier-based aircraft. Currently Russian Naval Aviation operates around 24 of these carrier-based aircraft. Considering that Russia has only one aircraft carrier, this quantity seems to be more than enough. Also recently Russian Navy ordered a regiment of shipborne version of the Mikoyan MiG-29 multi-role fighter. It appears that the Russian Navy prefers the lighter MiG-29K to the Su-33 due to its lower price and lower servicing costs. However the MiG-29K is not that capable.
For a long time Russia was proposing the Su-33 for export and some negotiations are currently in process. China was interested in obtaining a few dozen of Sukhoi Su-33 fighters for their aircraft carrier. A purchase of 50 Sukhoi Su-33 was negotiated for an amount of $2.5 billion in 2006. But eventually these negotiations between the two states fell through. The deal collapsed when it became clear that the Chinese violated the intellectual property agreement and developed their own version of this aircraft, known as the Shenyang J-15.
In 2004, Russia made a deal to refurbish and upgrade a former Kiev class aircraft carrier and sell it to India, where it is known as Vikramaditya. Russia made them an offer to sell the Sukhoi Su-33 to accompany the vessel. However the Indian Navy decided to purchase Mikoyan MiG-29 aircraft instead as they were more compact, thus more suitable to the carrier. As both deals with China and India fell through, Russia is still the sole operator of Sukhoi Su-33.
Compared to other air-superiority fighters, like Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet, the Su-33 is superior in some areas, including the maximum speed, service ceiling and the rate of climb. Su-33’s two AL-31F3 turbofans generate a dry thrust of 74.5 kN, each while the maximum thrust with afterburner is 125.5 kN for each engine. Top speed is 2 300 km/h at the altitude of 10 kilometers.
The Su-33 aircraft has not been used in combat. However some of them were lost due to accidents.



General characteristics
Crew: 1
Length: 21.19 m (69 ft 6 in)
Wingspan: 14.7 m (48 ft 3 in)
Height: 5.93 m (19 ft 6 in)
Wing area: 67.84 m² (730 ft²)
Empty weight: 18,400 kg (40,600 lb)
Loaded weight: 29,940 kg (66,010 lb)
Max. takeoff weight: 33,000 kg (72,752 lb)
Powerplant: 2 × Saturn AL-31F3 afterburning turbofans
Dry thrust: 74.5 kN (16,750 lbf) each
Thrust with afterburner: 125.5 kN (28,214 lbf) each
Performance
Maximum speed: Mach 2.2 (2,300 km/h; 1,430 mph) at 10,000 m (33,000 ft)
Stall speed: Mach 0.19 (240 km/h; 150 mph)
Range: 3,000 km (1,864 mi)
Service ceiling: 17,000 m (55,800 ft)
Rate of climb: 246 m/s (48,500 ft/min)
Wing loading: 483 kg/m² (98.9 lb/ft²)
Thrust/weight: 0.83
Maximum g-load: +8 g
Landing speed: 240 km/h, 149 mph
Armament
Guns: 1 × 30 mm Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-301 autocannon with 150 rounds
Hardpoints: 12 × external hardpoints with a capacity of up to 6,500 kg (14,300 lb) of ordnance and provisions to carry combinations of:
Rockets:
S-8KOM/BM/OM
S-13T/OF
S-25OFM-PU
Missiles:
Air-to-air missiles:
8 × R-27R/ER/T/ET
4 × R-73E
Anti-ship missiles:
Kh-31A
Kh-41
Anti-radiation missiles:
Kh-25MP
Kh-31P
Bombs:
RBK-500 cluster bomb
Up to 500 kg (1,100 lb) bombs
Avionics
Bars planar array radar
OEPS-27 electro-optical targeting system
SVP-24 electro-optical targeting system
Role: Carrier-based air superiority fighter and multirole fighter
National origin: Soviet Union / Russia
Manufacturer: Sukhoi
First flight: 17 August 1987
Introduction: 31 August 1998 (official)
Status: In service
Primary user: Russian Navy
Produced: 1987-1999
Number built: approx. 35
Developed from: Sukhoi Su-27