S'sonic
Stealth
Menu
A free template by Lucknowwebs.com for WYSIWYG WebBuilder 8
Powered by Sispro1-S
Nigel G Wilcox
Paragon Of Space Publication
© Copyright Reserved - United Kingdom
Ideal Screen Composition 1024 x 768
SITEMAP
PSEUDO SCIENCE
SCIENCE RESEARCH
ABOUT
Desk
Supersonic
Stealth
Study
Menu
MAIN INDEX
Fastest Air Planes
Space
Transport
Menu
http://military.wikia.com/wiki/SEPECAT_Jaguar?file=Cockpit_of_Jaguar_GR.3A.jpg
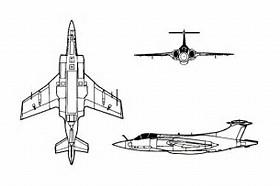
Blackburn Buccaneer
The Blackburn Buccaneer was a British carrier-borne attack aircraft designed in the 1950s for the Royal Navy. Designed and initially produced by Blackburn Aircraft at Brough, it was later officially known as the Hawker Siddeley Buccaneer when Blackburn became a part of the Hawker Siddeley Group, but this name is rarely used.
Maximum speed: 1,073 km/h (666.98 mph) Maiden flight: 30 Apr 1958 Length: 63.42 ft Wingspan: 44.00 ft Introduced: 1959 Retired: 1993
General characteristics
Crew: 2 (Pilot and Observer)
Length: 63 ft 5 in (19.33 m)
Wingspan: 44 ft (13.41 m)
Height: 16 ft 3 in (4.97 m)
Wing area: 514.7 ft² (47.82 m²)
Empty weight: 30,000 lb (14,000 kg)
Loaded weight: 62,000 lb (28,000 kg)
Powerplant: 2 × Rolls-Royce Spey Mk 101 turbofans, 11,100 lbf (49 kN) each
Performance
Maximum speed: 667 mph (580 kn, 1,074 km/h) at 200 ft (60 m)
Range: 2,300 mi (2,000 nmi, 3,700 km)
Service ceiling: 40,000 ft (12,200 m)
Wing loading: 120.5 lb/ft² (587.6 kg/m²)
Thrust/weight: 0.36
Armament
Hardpoints: 4 × under-wing pylon stations for up to 4,000 lb (1,814 kg) of bombs, & 1 × internal rotating bomb bay with a capacity of 12,000 lb (5,443 kg) and provisions to carry combinations of:
Rockets: 4 × Matra rocket pods with 18 × SNEB 68 mm rockets each
Missiles: 2 × AIM-9 Sidewinders for self-defence or 2 × AS-37 Martel missiles or 4 × Sea Eagle missile
Bombs: Various unguided bombs, laser-guided bombs, as well as the Red Beard or WE.177 tactical nuclear bombs
Other: AN/ALQ-101 ECM protection pod, AN/AVQ-23 Pave Spike laser designator pod, buddy refuelling pack or drop tanks for extended range/loitering time
Variants: -
Buccaneer S.1
First Production aircraft, powered by DH Gyron Jr turbojets, 40 built.
Buccaneer S.2
Development of S.1, powered by Rolls Royce Spey turbofans, 84 built.
Buccaneer S.2A
Royal Navy S.2 modified for the Royal Air Force.
Buccaneer S.2B
Modified S.2 for Royal Air Force capable of carrying Martel missile, 46 built.
Buccaneer S.2C
Royal Navy aircraft upgraded to S.2A.
Buccaneer S.2D
Royal Navy aircraft upgraded to S.2B.
The Blackburn Aeroplane and Motor Company changed its name to Blackburn Aircraft Limited in 1936 and joined forces with Maurice Denny, a Dumbarton Shipbuilder to establish a new Blackburn Factory at Barge Park, Dumbarton for the production of the Blackburn Botha. Before and during WWII, Blackburn Aircraft (Dumbarton) produced 250 Shorts Sunderland Flying Boats as well as preparing and converting many American aircraft for use by the Fleet Air Arm
Blackburn merged with General Aircraft Limited in 1949 and was renamed Blackburn and General Aircraft Limited. Despite seeing a reasonable success with the Blackburn Beverley (based on the GAL.60 Universal Freighter) by 1958 the company reverted back to Blackburn Aircraft Limited.
The bulk of the manufacturing was concentrated on the factory at Brough in the East Riding of Yorkshire where they made a huge number of different designs ranging from the propeller-driven General Aircraft GAL.60/65 Beverley heavy-lift transport to the Blackburn Buccaneer sub sonic jet strike aircraft in 1958.
Finally, the company was absorbed into Hawker Siddeley in 1960 and the Blackburn name disappeared in 1963.
The first production model the S.1, was powered by two DH Gyron Jr turbojets each producing 7,100 lbf of thrust, which proved underpowered when fully armed and fuelled.
A temporary solution to enable the S.1 to take off fully armed was to take off with a minimum fuel load and then refuel in mid air.
To overcome the power deficit the Buccaneer was fitted with twin Rolls Royce Spey turbofans with the nacelles being increased in size to accomodate them. This modification was designated the Buccaneer S.2 and it replaced the S.1 by late 1966.
The Buccaneer was adopted by the Royal Air Force in 1968 with a total of 46 aircraft being built by Hawker Siddeley. The aircraft, designated S.2B, had RAF specification communications and avionics and capable of carrying an additional fuel tank in the bomb bay.
The self-defence capability of the RAF Buccaneer consisted of an AN/ALQ-101 ECM pod, chaff/flare dispenser and able to carry AIM-9 sidewinder missiles.
Low level strike aircraft could carry four 1,000lb retarded bombs that could be dropped as a deterrent against any following aircraft.
The RAF Buccaneer could also act as a target designator for other Buccaneers, Jaguars and other strike aircraft with the use of the AN/AVQ-23E Pave Spike laser designated pod for paveway II guided bombs.
Some Buccaneers in service with the Fleet Air Arm were modified to enable them to carry the Martel anti-ship missile, designated S.2D. The remainder of the Fleet Aior Arm Buccaneers were designated S.2C.
The Fleet Air Arm Buccaneers was also type approved to carry nuclear weapons, such as Red Beard and WE.177 drop-bombs.
On the 28th of March 1967, the shipwrecked supertanker 'Torrey Canyon' was bombed by Buccaneers from HMS Lossiemouth to vapourise the oil and help avoid an environmental disaster.









Role: Maritime strike aircraft
National origin: United Kingdom
Manufacturer: Blackburn Aircraft Limited,
Hawker Siddeley
First flight: 30 April 1958
Introduction: 17 July 1962
Retired: 31 March 1994
Primary users: Royal Navy
Royal Air Force
South African Air Force
Number built: 211