S'sonic
Stealth
Menu
A free template by Lucknowwebs.com for WYSIWYG WebBuilder 8
Powered by Sispro1-S
Nigel G Wilcox
Paragon Of Space Publication
© Copyright Reserved - United Kingdom
Ideal Screen Composition 1024 x 768
SITEMAP
PSEUDO SCIENCE
SCIENCE RESEARCH
ABOUT
Desk
Supersonic
Stealth
Study
Menu
MAIN INDEX
Fastest Air Planes
Space
Transport
Menu
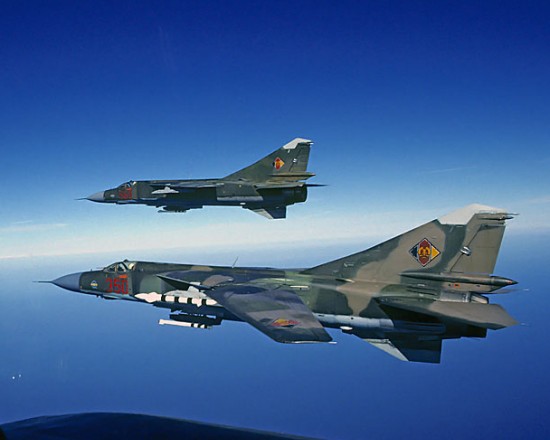
Mikoyan-Gurevich-Mig-23
A Soviet Air Force MiG-23MLD
Role: Fighter aircraft (M series)
Fighter-bomber (B series)
National origin: Soviet Union
Manufacturer: Mikoyan-Gurevich / Mikoyan
First flight: 10 June 1967
Introduction: 1970
Status: In limited service
Primary users: Soviet Air Force (historical)
Syrian Air Force
Indian Air force (historical)
Bulgarian Air Force (historical)
Produced: 1967-1985
Number built: 5,047
Variants: Mikoyan MiG-27
According to the MiG-23ML manual, the MiG-23ML has a maximum sustained turn rate of 14.1 deg/sec and a maximum instantaneous turn rate of 16.7 deg/sec. The MiG-23ML accelerates from 600 km/h (373 mph) to 900 km/h (559 mph) in 12 seconds at the altitude of 1000 meters. The MiG-23 accelerates at the altitude of 1 km from 630 km/h (391 mph) to 1300 km/h (808 mph) in 30 seconds and at the altitude of 10-12 km will accelerate from Mach 1 to Mach 2 in 160 seconds.

General characteristics
Crew: 1
Length: 15.65 m (51 ft 4 in)
Wingspan:
With wings spread: 13.965 m (45 ft 10 in)
With wings swept: 7.779 m (25 ft 6 in)
Height: 4.82 m (15 ft 9.75 in)
Wing area:
With wings spread: 37.35 m² (402 ft²)
With wings swept: 34.16 m² (367.7 ft²)
Empty weight: 9,595 kg (21,153 lb)
Loaded weight: 14,700 kg (32,400 lb)
Max. takeoff weight: 17,800 kg (39,230 lb)
Powerplant: 1 × Khatchaturov R-35-300 afterburning turbojet Dry thrust: 83.6 kN (18,850 lbf)
Thrust with afterburner: 127 kN (28,700 lbf)
Performance
Maximum speed: At altitude: Mach 1.52 (1,880 km/h; 1,168 mph)
At sea level: Mach 0.89 (1,100 km/h; 684 mph)
Range: 1,150 km (710 mi; 620 nmi)
Combat radius: 600 km (370 mi; 320 nmi) at low-level combat (lo-lo-lo) with 4 × 250 kg (550 lb) bombs
Ferry range: 2,820 km (1,750 mi; 1,520 nmi)
Service ceiling: 18,500 m (60,695 ft)
Rate of climb: 240 m/s (47,245 ft/min)
Wing loading: With wings spread: 476.6 kg/m² (97.7 ft/lb²)
With wings swept: 521 kg/m² (106.8 lb/ft²)
Thrust/weight: 0.88
Maximum g-load: 8.5 g
Armament
Guns: 1 × 23 mm Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-23L autocannon with 260 rounds
Hardpoints: 2 × fuselage, 2 × wing glove and 2 × wing pylons with a capacity of up to 3,000 kg (6,600 lb) of stores and provisions to carry combinations of: Rockets: S-5
Missiles:
Air-to-air missiles: 2 × R-60
R-73
2 × R-23
R-77
2 × R-27R
Air-to-surface missiles: Kh-23 Grom
Bombs: Up to 500 kg (1,100 lb) bombs
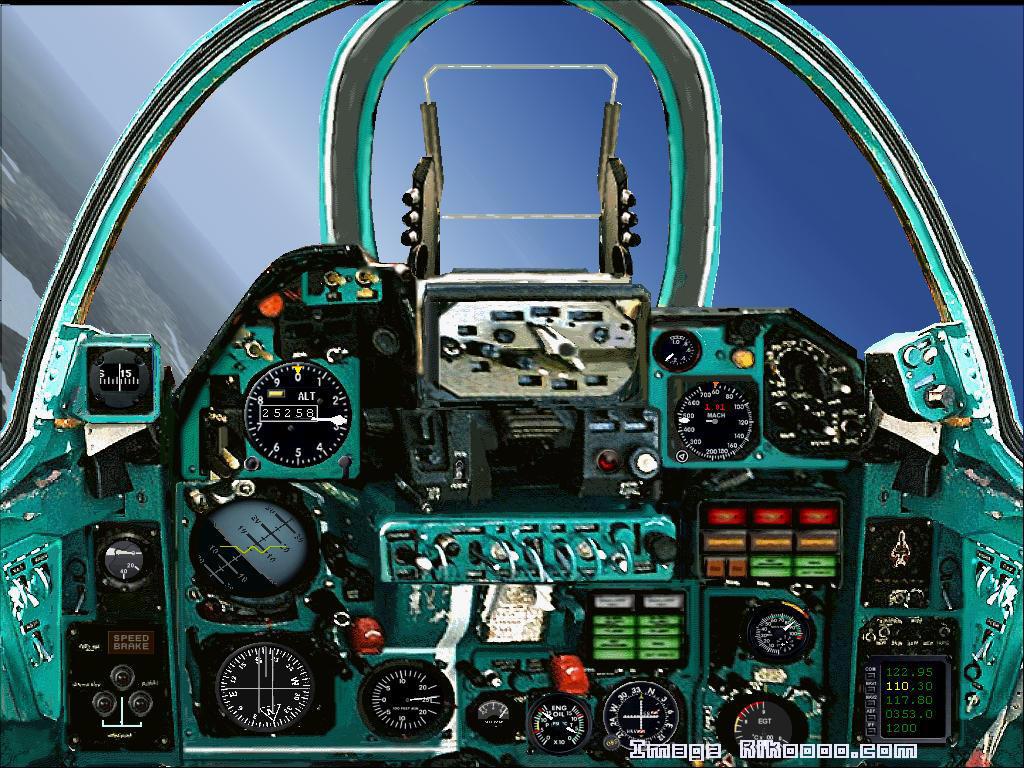
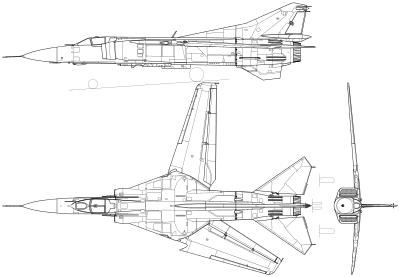




The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23 (Russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-23; NATO reporting name: Flogger) is a variable-geometry fighter aircraft, designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich design bureau in the Soviet Union. It is considered to belong to the Soviet third-generation jet fighter category, along with similarly aged Soviet fighters such as the MiG-25 "Foxbat". It was the first attempt by the Soviet Union to design look-down/shoot-down radar and one of the first to be armed with beyond visual range missiles. Production started in 1970 and reached large numbers with over 5,000 aircraft built. Today the MiG-23 remains in limited service with some export customers.
The basic design was also used as the basis for the Mikoyan MiG-27, a dedicated ground-attack variant. Among many minor changes, the MiG-27 replaced the MiG-23's nose-mounted radar system with an optical panel holding a laser designator and a TV camera.
An adept interceptor with fighter capabilities a level above those featured in the MiG-21 preceding it, especially range, the MiG-23 was nicknamed the "Flogger" by NATO for it could easily engage (and down) the best fighters the west had to offer. Like many Soviet fighters, it was developed in a multitude of variants, some of which still serve today. MiG-23s also belong to the elite club of aircraft that have seen continuous combat, and "Floggers" have preyed on MiG-21s, Mirage F1s, Northrop F-5s, F-4 Phantoms, and even several of Iran's fabled F-14 Tomcats (Floggers saw much less success against American F-14s) in the middle eastern theatre. The one time muscle of the entire Soviet Air Defence (SAD) command, the MiG-23 is slowly being phased out of service but still remains in service with many air forces lacking the funds for modern fighters. Several upgrade programmes were offered to remedy this and certain countries may keep their examples in service up until 2015.
It should be noted that through most of the Cold War, the MiG-23 was thought to be nothing more than a "serviceable" and "highly utilitarian" aircraft at best. It was only some decades later that the old Western observations were upgraded to conclude that the MiG-23 was an impressive design in its own right, one that could match or (in some cases) out-best many of the available Western counterparts of the time.
23 is a variable-geometry fighter aircraft, designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich design bureau in the Soviet Union. It is considered to belong to the Soviet third-generation jet fighter category, along with similarly aged Soviet fighters such as the MiG-25 "Foxbat". It was the first attempt by the Soviet Union to design look-down/shoot-down radar and one of the first to be armed with beyond visual range missiles. Production started in 1970 and reached large numbers with over 5,000 aircraft built. Today the MiG-23 remains in limited service with some export customers.
Maiden flight: 10 Jun 1967 Length: 54.79 ft Wingspan: 45.83 ft Passengers: 2 Introduced: 1970 Manufacturer: Russian Aircraft Corporation MiG