S'sonic
Stealth
Menu
A free template by Lucknowwebs.com for WYSIWYG WebBuilder 8
Nigel G Wilcox
Powered by Sispro1-S
Paragon Of Space Publication
© Copyright Reserved - United Kingdom
Ideal Screen Composition 1024 x 768
SITEMAP
PSEUDO SCIENCE
SCIENCE RESEARCH
ABOUT
Desk
Supersonic
Stealth
Study
Menu
MAIN INDEX
Fastest Air Planes
Space
Transport
Menu
F-101B Voodoo
The McDonnell F-101 Voodoo was a supersonic jet fighter which served the United States Air Force and the Royal Canadian Air Force. Initially designed by McDonnell Aircraft as a long-range bomber escort for the Strategic Air Command, the Voodoo was instead developed as a nuclear-armed fighter-bomber for the Tactical Air Command, and as a photo reconnaissance aircraft based on the same airframe. An F-101A set a number of world speed records for jet powered aircraft, including fastest airspeed, attaining 1,207.6 miles per hour on 12 December 1957. They operated in the reconnaissance role until 1979.
Maiden flight: 29 Sep 1954 Length: 67.42 ft Wingspan: 39.67 ft Introduced: May 1957 Retired: 1966 Passengers: 2
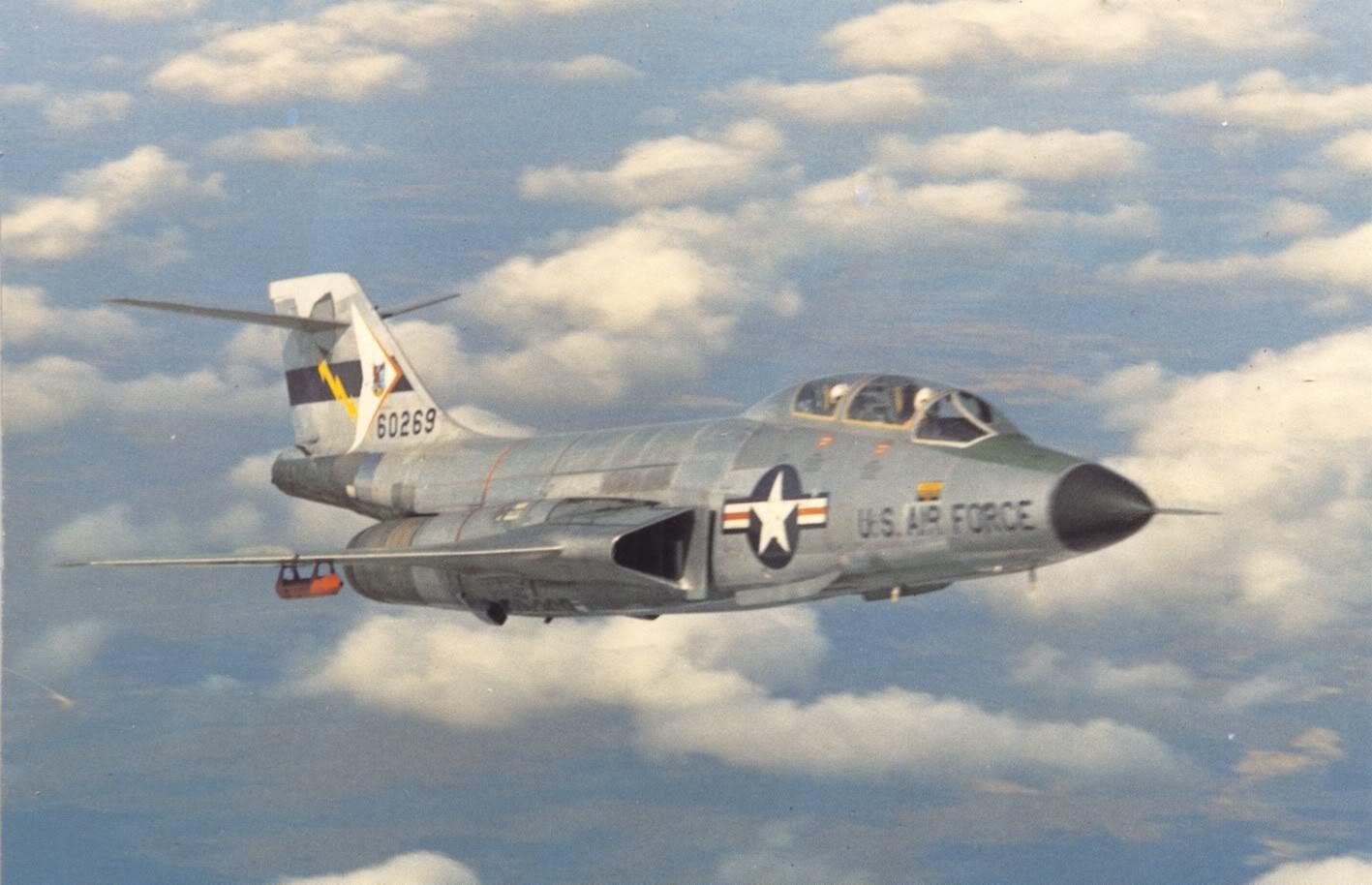




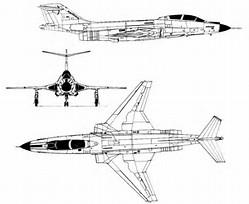





The F-101B Voodoo (designated CF-101B in the RCAF) was built by McDonnell Aircraft Corporation of St. Louis, Missouri in 1957 as a follow on to its earlier F-88 model. It was powered by two axial flow Pratt & Whitney J57 turbojet engines with afterburners. In the interceptor role, a fire-control radar is operated by the navigator in the rear cockpit, with either manual or data-link control. The Voodoo was used during the Vietnam War to fly reconnaissance and combat missions.
The Royal Canadian Air Force maintained a stockpile of AIR-2A Genie unguided nuclear air-to-air rockets as the primary wartime weapon on the CF-101 Voodoo all-weather interceptor after 1965. The rockets were held by detachments of the United States Air Force at the Canadian Voodoo bases, and would have been released to Canada if conflict threatened. These were removed in 1984, when the F-18 Hornet entered squadron service and the Voodoo was retired.
In 1960, following the Arrow cancellation, it was decided to replace the Canadian CF-100 all weather fighter with the Voodoo. A total of 66 aircraft were acquired. In 1970 these aircraft were replaced by other overhauled, refurbished and modernized Voodoos. For 25 years, until 1985, Voodoos provided all weather air defense through the North American Air Defense (NORAD) Agreement, using both conventional and nuclear weapons.
Role: Fighter aircraft
Manufacturer: McDonnell Aircraft
First flight: 29 September 1954
Introduction: May 1957
Retired: 1972, USAF 1982, US ANG 1984, Canada
Primary users: United States Air Force
Royal Canadian Air Force
Number built: 807
Unit cost: US$1,276,145 (RF-101C) US$1,754,066 (F-101B)[2]
Developed from: XF-88 Voodoo
Variants: McDonnell CF-101 Voodoo
General characteristics
Crew: 2
Length: 67 ft 5 in (20.55 m)
Wingspan: 39 ft 8 in (12.09 m)
Height: 18 ft 0 in (5.49 m)
Wing area: 368 ft² (34.20 m²)
Airfoil: NACA 65A007 mod root, 65A006 mod tip
Empty weight: 28,495 lb (12,925 kg)
Loaded weight: 45,665 lb (20,715 kg)
Max. takeoff weight: 52,400 lb (23,770 kg)
Internal fuel capacity: 2,053 gal (7,771 l) or 2,953 gal (11,178 l) with two external tanks
Powerplant: 2 × Pratt & Whitney J57-P-55 afterburning turbojets
Dry thrust: 11,990 lbf (53.3 kN) each
Thrust with afterburner: 16,900 lbf (75.2 kN) each
Performance
Maximum speed: Mach 1.72 (1,134 mph, 1,825 km/h) at 35,000 ft (10,500 m)
Range: 1,520 mi (1,320 nm, 2,450 km)
Service ceiling: 58,400 ft (17,800 m)
Rate of climb: 49,200 ft/min (250 m/s)
Wing loading: 124 lb/ft² (607 kg/m²)
Thrust/weight: 0.74
Armament
Missiles: 4 (originally 6)× AIM-4 Falcon, or 2× AIR-2 Genie nuclear rockets, plus 2× AIM-4 Falcon
note: Falcon missile variants - AIM-4A, AIM-4B, AIM-4C only. The range was about 5 mi (8 km).
Avionics
Hughes MG-13 fire control system