General characteristics
Crew: 2
Length: 23.34 m (72 ft 2 in)
Wingspan: 14.7 m (48 ft 3 in)
Height: 6.09 m (19 ft 5 in)
Wing area: 62.04 m² (667.8 ft²)
Empty weight: 22,500 kg (49,608 lb)
Loaded weight: 39,000 kg (85,980 lb)
Max. takeoff weight: 45,100 kg (99,425 lb)
Internal fuel: 12,100 kg (15,400 l)
Powerplant: 2 × Saturn AL-31FM1 turbofans
Maximum speed: At high altitude: Mach 1.8+ (~2,000 km/h, 1,200 mph)
At sea level: Mach 1.2 (1,400 km/h, 870 mph)
Performance
Range: 1,100 km (680 mi; 590 nmi) at low altitude
Combat radius: 1,000 km (680 mi; 540 nmi)
Ferry range: 4,000 km (2,490 mi; 2,160 nmi)
Service ceiling: 15,000 m (49,200 ft)
Thrust/weight: 0.68
Maximum g-load: 9 g
Armament
Guns: 1 × 30 mm Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-301 autocannon with 180 rounds
Hardpoints: 12 × wing and fuselage pylons with a capacity of 8,000-12,000 kg (17,600-26,500 lb) and provisions to carry combinations of:
Rockets:
B-8 rocket pods for 20 × S-8KOM/OM/BM
B-13 rocket pods for 5 × S-13T/OF
O-25 rocket pods for 1 × S-25OFM-PU
S-80FP
Missiles:
Air-to-air missiles:
2 × R-27R/ER/T/ET
2 × R-73E
2 × RVV-AE
Air-to-surface missiles:
Kh-29L/T/D
Kh-38MAE/MKE/MLE/MTE
Kh-25ML/MT
Kh-59ME/MK/MK2
Kh-58
Anti-ship missiles:
Kh-31A/AD
Kh-35U
P-800 Oniks weight of 1500 kg with a range of up to 300 km and a speed in the range of numbers M = 2.2-3.0. Officially not in service.
Kh-41
Anti-radiation missiles:
Kh-25MP
Kh-58
Kh-31P/PD
Cruise missiles:
Kh-36
Kh-65S/SE
Kh-SD
Bombs:
KAB-500KR TV-guided bomb
KAB-500L laser-guided bomb
KAB-500OD guided bomb
KAB-500S-E satellite-guided bomb
KAB-1500KR TV-guided bomb
KAB-1500L laser-guided bomb
OFAB-250-270 bomb
OFAB-100-120 bomb
FAB-500T general-purpose bomb
2 × BETAB-500SHP
P-50T bomb
ODAB-500PM bomb
RBK-500 cluster bomb
SPBE-D bomb
Avionics
V004 passive electronically scanned array radar
Khibiny electronic countermeasures system
SAP-14 electronic coutermeasures system
SAP-518 electronic coutermeasures system
UKR-RT radio surveilance system
S'sonic
Stealth
Menu
A free template by Lucknowwebs.com for WYSIWYG WebBuilder 8
Nigel G Wilcox
Powered by Sispro1-S
Paragon Of Space Publication
© Copyright Reserved - United Kingdom
Ideal Screen Composition 1024 x 768
SITEMAP
PSEUDO SCIENCE
SCIENCE RESEARCH
ABOUT
Desk
Supersonic
Stealth
Study
Menu
MAIN INDEX
Fastest Air Planes
Space
Transport
Menu
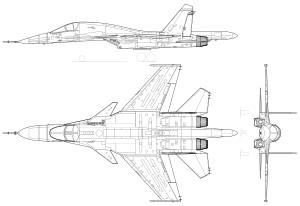
Sukhoi Su-34
The Sukhoi Su-34 is a Russian twin-engine, twin-seat, all-weather supersonic medium-range fighter-bomber. It is intended to replace the Sukhoi Su-24 and first entered service in 2014 with the Russian Air Force.
Maximum speed: 2,200 km/h (1,367 mph) Range: 2,485 mi Maiden flight: 13 Apr 1990 Length: 76.57 ft Wingspan: 48.26 ft Passengers: 2
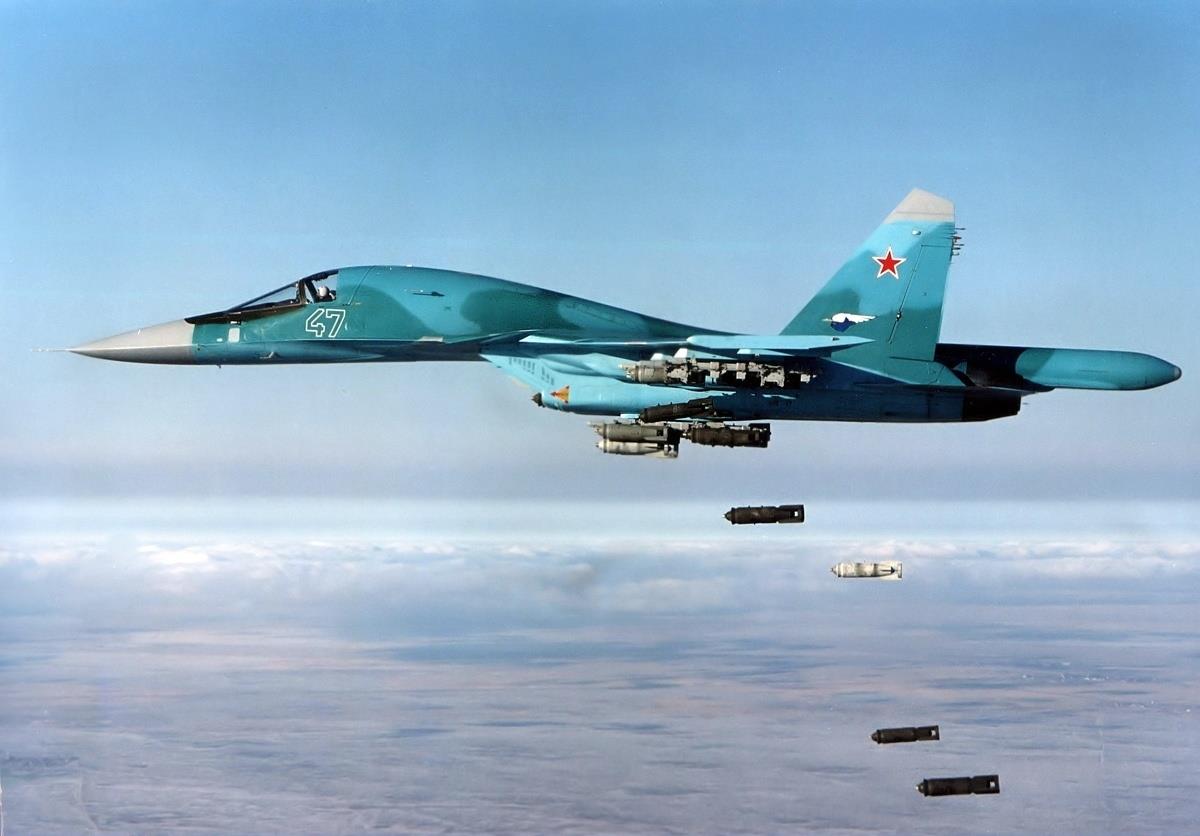








Also known as Su-27IB, the Su-34 fighter bomber has been developed by the Sukhoi Design Bureau Joint Stock Company, Moscow and the Novosibirsk Aircraft Production Association at Novosibirsk, Russia.
The Russian Air Force ordered an initial 32 Su-34 aircraft in 2008, with an additional requirement for 92 aircraft in 2012. The first two production aircraft were delivered to the Russian Air Force in December 2006. The export designation of the Su-34 is Su-32.
Production of the Su-34 bomber
Full-rate production began in January 2008. In the same month, the Russian Air Force stated that 70 aircraft would be secured by 2015.
Under a state contract with the Russian Ministry of Defence, Sukhoi will deliver the Su-34 bombers to the Russian Air Force and army units until 2020.
The Russian Air Force received two Su-34 aircraft in December 2009. Four more Su-34 fighter-bombers were provided in December 2010.
Sukhoi's Novosibirsk aircraft plant handed over another two Su-34s in December 2011. Five Su-34 aircraft were supplied in December 2012.
The company also delivered five Su-34 frontline bombers to the Russian Air Force in January 2013, and a batch of Su-34 frontline bombers were distributed in October 2013.
Sukhoi transferred the final consignment of Su-34 front-line bombers to the Russian Air Force in December 2013, concluding the five-year state contract signed in 2008.
Under the 2014 State Defence order, Sukhoi released the first set of serial Su-34 frontline bombers to the Russian Air Force in June 2014. The second batch was delivered in July 2014 and a further delivery of Su-34 bombers was made in October 2014. An additional two bombers were handed over in December 2014.
Under the 2015 state defence order, Sukhoi provided the first two batches of Su-34 aircraft to the Russian Ministry of Defence (MoD) in May 2015.
An additional batch of Su-34 bombers was delivered to the MoD in November 2015. The firm concluded the 2015 state defence order with the delivery of two aircraft in December 2015.
Following the 2016 state defence order, Sukhoi handed over three batches of Su-34 frontline bombers to the Russian Air Force in 2016.
Su-27 Flanker based design of the Su-34
The Su-34 replaces the Tu-23M and Su-24 aircraft. It is one of a number of Russian aircraft based and developed from the Su-27 Flanker, including the Su-30, Su-33 and Su-35.
"The Su-34 fighter bomber is armed with a 30mm GSh-301 gun and 180 rounds of ammunition."
The Su-34 design retains the basic layout and construction of the Su-27 airframe, as well as the same conventional high-wing configuration and onboard equipment.
The Su-34, however, has a changed contour of the nose section to accommodate an advanced, multi-mode, phased array radar with terrain following and terrain avoidance modes. It has a two-seat rather than single-seat cockpit and capacity of the internal fuel tanks has been increased with a resulting increased take-off weight. Changes have been made to the central tail boom for rear-facing radar.
Su-34 cockpit
The cockpit has two K-36DM zero/zero ejection seats side-by-side for the pilot and co-pilot. The seats are supplied by Zvesda Research and Production Enterprise Joint Stock Company, Moscow. The multifunction displays in the cockpit show the flight parameters, the operational status of the aircraft units, and tactical data.
Weapons onboard the Su-34
Su-33 Flanker-D Carrier-Based Fighter, Russia
The Su-33 is a single-seat multirole carrier-based conventional take-off and landing (CTOL) fighter aircraft.
The Su-34 is armed with a 30mm GSh-301 gun and 180 rounds of ammunition. The gun has a maximum rate of fire of 1,500 rounds a minute and the muzzle velocity is 860m/s. It is supplied by the Instrument Design Bureau, Tula.
The aircraft has ten hardpoints for weapon payloads and is able to carry a range of missiles, including air-to-air, air-to-surface, anti-ship and anti-radiation missiles, guided and unguided bombs, and rockets. The aircraft is fitted with a target designator.
The R-73, Nato codename AA-11 Archer, short-range, air-to-air missile is supplied by the Vympel State Engineering Design Bureau, Moscow. The R-73 is an all-aspect missile capable of engaging targets in tail-chase or head-on mode. The missile has cooled infrared homing.
The R-73 attacks the target within target designation angles of ±45° and with angular rates up to 60° a second. The missile can intercept targets at altitudes between 0.02km and 20km, and target G-load to 12g, with target speeds of up to 2,500km/h.
Also known as the RR-77 or by the Nato designation AA-12, the RVV-AE long-range air-to-air missile is manufactured by Vympel. The missile can intercept targets at speeds up to 3,600km/h and altitudes from 0.02km to 25km. The minimum range in the aft hemisphere is 300m and the maximum vertical separation between the host aircraft and the target is 10km.
The RR-77 has inertial guidance with mid-course radio updates and terminal active guidance. A new, longer-range (150km) version of the R-77, with solid fuel ram-jet propulsion, is being tested by Vympel.
The Su-34 carries a range of precision-guided and unguided bombs and rockets, including the KAB-500 laser-guided bomb developed by the Region State Research and Production Enterprise, Moscow.
Systems of the Su-34
The Su-34 is equipped with an electro-optical fire control system, supplied by the Urals Optical and Mechanical Plant (YOM3), and a Geofizika FLIR pod, with forward-looking infrared. Leninetz of St Petersburg supplies the passive phased array radar system and TsNIRTI the electronic countermeasures suite.
Engines and performance
"The aircraft can carry 12,100kg of fuel internally in two fuel tanks in the wings and four in the fuselage."
First production aircraft are powered by two after-burning NPO Saturn AL-31F turbofan engines. Later aircraft may be fitted with MMPP Salyut AL-31F-M2/3 or NPO Saturn 117 engines. They are mounted under the wing and are equipped with all-duty fixed geometry air intakes. A rotor protection installed in the air intakes provides protection against the ingestion of foreign objects.
Internally, the aircraft can carry 12,100kg of fuel in two fuel tanks in the wings and four in the fuselage. Three external 3,000l fuel tanks can also be fitted.
The aircraft can achieve a speed of 1,900km/h (Mach 1.6) at altitude and 1,300km/h (Mach 1) at sea level, and has a flight range of 4,000km.
Crew: Two
Length: 23.34m
Height: 6.36m
Wingspan: 14.05m
Normal Take-Off Weight: 39,999kg
Maximum Take-Off Weight: 45,100kg
Normal Combat Load Weight: 4,000kg
Role: Fighter-bomber, strike fighter
National origin: Russia
Manufacturer: Sukhoi
First flight: 13 April 1990
Introduction: 20 March 2014
Status: In service
Primary user: Russian Air Force
Produced: 2006-present
Number built: 102 as of May 2017
Unit cost: US$36 million
Developed from: Sukhoi Su-27